The lithium battery protection circuit board is mainly composed of protection IC (overvoltage protection) and MOS tube (overcurrent protection), and is a device used to protect the safety of lithium battery cells. Lithium batteries are widely used by people for their large discharge current, low internal resistance, long life, and no memory effect. Lithium-ion batteries are strictly prohibited from overcharging, overdischarging, and short-circuiting during use, otherwise it will cause the battery to catch fire and explode. Therefore, when using rechargeable lithium batteries, there will be a protective circuit board to protect the safety of the batteries.
Working principle of battery protection circuit board
Lithium-ion battery protection circuit boards have different circuits and parameters according to different ICs, voltages, etc. The commonly used protection ICs are 8261, DW01+, CS213, GEM5018, etc. Among them, Seiko's 8261 series have better accuracy and of course the price is more expensive. The latter are all produced in Taiwan. The domestic secondary market basically uses DW01+ and CS213. The following is an explanation with DW01+ with MOS tube 8205A (8pin):
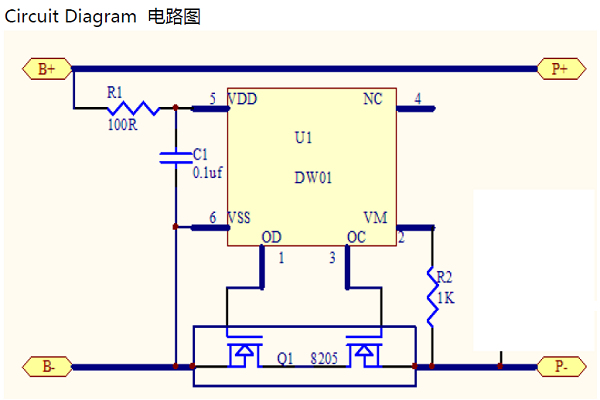
The normal working process of the lithium-ion battery protection circuit board is:
When the cell voltage is between 2.5V and 4.3V, the first pin and the third pin of DW01 both output high level (equal to the supply voltage), and the second pin voltage is 0V. At this time, the voltage of pin 1 and pin 3 of DW01 will be applied to pins 5 and 4 of 8205A respectively. The two electronic switches in 8205A are in the conducting state because their G poles are connected to the voltage from DW01, that is Both electronic switches are in the open state. At this time, the negative pole of the battery is directly connected to the P- terminal of the protection board, and the protection board has a voltage output.
Protection circuit board over-discharge protection control principle:
When the cell is discharged through an external load, the voltage of the cell will slowly decrease. At the same time, the DW01 will monitor the cell voltage in real time through the R1 resistance. When the cell voltage drops to about 2.3V, DW01 will consider that the cell voltage has been In the over-discharge voltage state, immediately disconnect the output voltage of the first pin, so that the voltage of the first pin becomes 0V, and the switch tube in the 8205A is closed because there is no voltage on the fifth pin. At this time, the B- of the battery cell and the P- of the protection board are in a disconnected state. That is, the discharge circuit of the battery cell is cut off, and the battery cell will stop discharging. The protection board is in an over-discharged state and has been maintained. After the P and P- of the protection board have indirect charging voltages, DW01 will immediately stop the over-discharge state after B- detects the charging voltage, and output a high voltage at pin 1 again to turn on the over-discharge control tube in the 8205A. That is, the B- of the battery cell and the P- of the protection board are reconnected, and the battery is directly charged by the charger.
Protection circuit board overcharge protection control principle:
When the battery is normally charged by the charger, as the charging time increases, the cell voltage will become higher and higher. When the cell voltage rises to 4.4V, DW01 will consider the cell voltage to be in an overcharge voltage state. It immediately disconnects the output voltage of the third pin, so that the voltage of the third pin becomes 0V, and the switch tube in the 8205A is closed because the fourth pin has no voltage. At this time, the B- of the battery cell and the P- of the protection board are in a disconnected state. That is, the charging circuit of the battery cell is cut off, and the battery cell will stop charging. The protection board is in an overcharged state and has been maintained. After the P and P- of the protection board discharge the load indirectly, although the overcharge control switch is turned off, the forward direction of the diode inside is the same as the direction of the discharge circuit, so the discharge circuit can be discharged. When the voltage of the battery cell When the voltage is lower than 4.3V, DW01 stops the overcharge protection state and outputs high voltage on pin 3 again, so that the overcharge control tube in 8205A is turned on, that is, the B- of the battery and the protection board P- are reconnected , The battery cell can be charged and discharged normally.
Principle of short-circuit protection control of protection circuit board:
In the process of external discharge of the protection circuit board, the two electronic switches in the 8205A are not completely equivalent to two mechanical switches, but are equivalent to two resistors with very small resistance, and are called the conduction internal resistance of the 8205A. The on-resistance of each switch is about 30m\U 03a9 and a total of about 60m\U 03a9. The voltage applied to the G pole actually directly controls the on-resistance of each switch. When the G pole voltage is greater than At 1V, the conduction resistance of the switch tube is very small (tens of milliohms), which is equivalent to the switch being closed. When the voltage of the G pole is less than 0.7V, the conduction resistance of the switch tube is very large (several MΩ), which is equivalent to The switch is off. The voltage UA is the voltage between the on-resistance of 8205A and the discharge current. When the load current increases, UA will inevitably increase. Because UA0.006L×IUA is also called the tube voltage drop of 8205A, UA can be abbreviated to indicate the size of the discharge current. . When it rises to 0.2V, it is considered that the load current has reached the limit value, so the output voltage of pin 1 is stopped, so that the voltage of pin 1 becomes 0V, the discharge control tube in 8205A is closed, and the discharge circuit of the cell is cut off. Discharge control tube. In other words, the maximum allowable output current of DW01 is 3.3A, which realizes over-current protection.
Short circuit protection control process:
Short-circuit protection is a limit form of over-current protection. Its control process and principle are the same as over-current protection. Short-circuit is only equivalent to adding a small resistance (about 0Ω) between P P- to make the protection board When the load current reaches more than 10A instantaneously, the protection circuit board immediately performs over-current protection.
The reason why lithium battery (rechargeable type) needs protection is determined by its own characteristics. Since the material of the lithium-ion polymer battery itself determines that it cannot be overcharged, overdischarged, overcurrent, short circuited, and ultra-high temperature charging and discharging, the lithium battery components always follow a delicate protection circuit board.


